Your arms do more than just lift, push, or pull—they are an essential part of your body’s strength, coordination, and daily functionality. Whether you’re reaching for something on a shelf, crushing a gym session, or typing away at your desk, your arm muscles are always at work.
In this detailed guide, we’ll break down the anatomy of your biceps, triceps, and forearms, explain how each muscle functions, and share the best exercises to help you build stronger, more defined arms that not only look great but also perform at their best.
🧠 Introduction to Arm Muscles
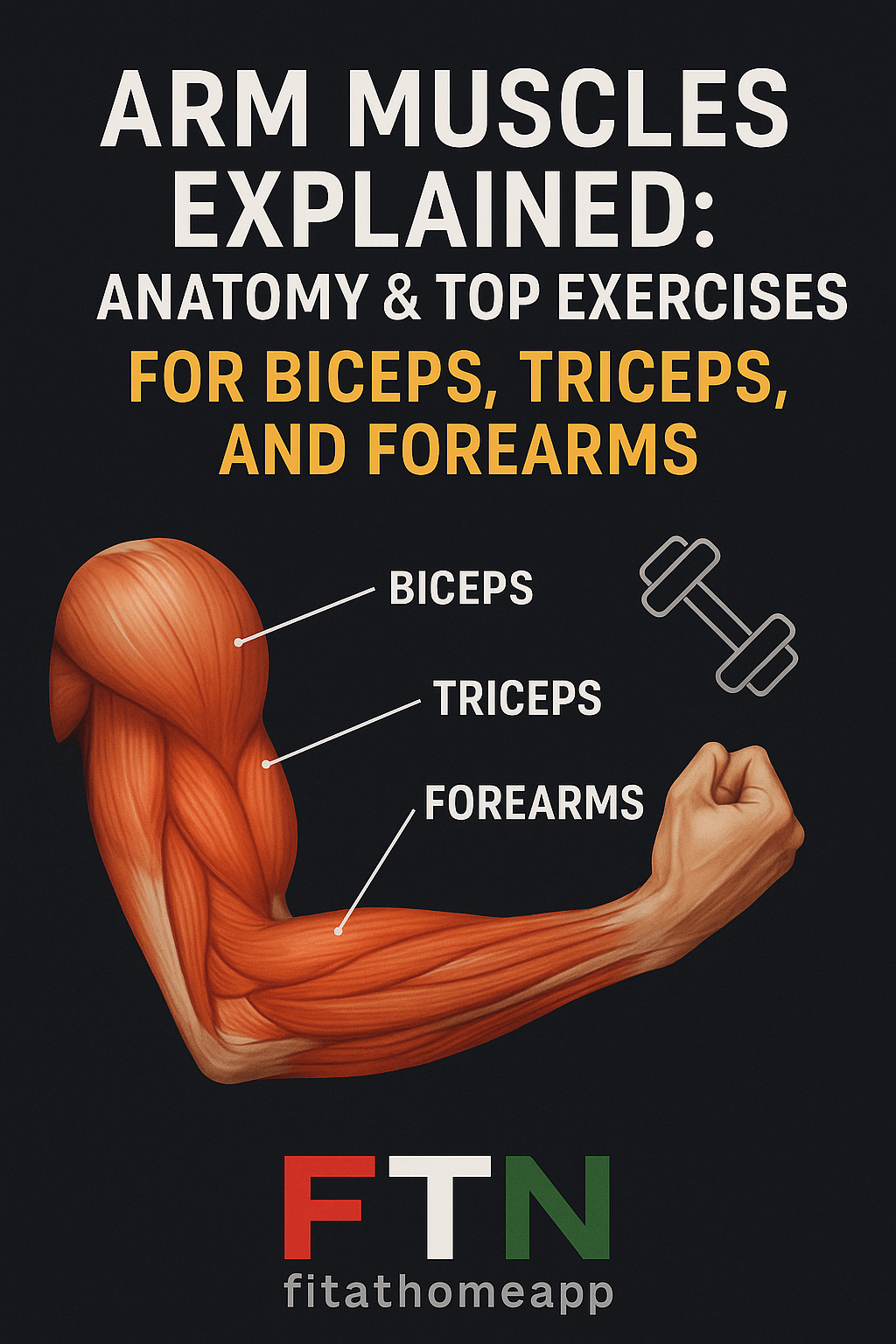
Your arm is made up of several muscle groups, but the three main areas you need to focus on are:
Biceps (front of the upper arm)
Triceps (back of the upper arm)
Forearms (lower arm muscles that control your grip and wrist)
Each of these muscles plays a vital role in daily activities like lifting, pushing, pulling, and rotating. From carrying groceries to playing sports, these muscles keep your upper body mobile, stable, and strong.
A well-balanced arm workout doesn’t just improve aesthetics—it enhances your overall functional strength 🏋️.
🔵 Anatomy of the Biceps
The biceps brachii, commonly known as the biceps, has two heads:
Long Head: originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of the shoulder blade
Short Head: originates from the coracoid process of the shoulder blade
These two heads converge into a single muscle belly and insert into the radius bone, allowing for:
Elbow flexion (bending your arm)
Forearm supination (rotating your palm upward)
💡 The short head gives the biceps a fuller look, while the long head helps create that famous “peak” when you flex. Developing both evenly ensures strength and symmetry.
🔴 Anatomy of the Triceps
On the back of your arm lies the triceps brachii, which consists of three heads:
Long Head (originates from the shoulder blade)
Lateral Head (from the outer humerus)
Medial Head (from the inner humerus)
All three heads insert into the olecranon of the ulna (elbow bone), making the triceps the primary elbow extensor.
Key Functions:
Extending the elbow (e.g., pushing movements)
Assisting with shoulder stability
Counterbalancing the biceps for controlled arm motion
💪 Strong triceps are essential for exercises like bench presses, push-ups, and dips, and they contribute significantly to upper arm size.
🟢 Anatomy of the Forearm Muscles
The forearm contains a complex network of muscles that control:
Wrist movement
Finger flexion and extension
Grip strength
It consists of two main compartments:
Anterior (Flexors): control wrist and finger flexion
Posterior (Extensors): control wrist and finger extension
Important muscles include:
Flexor carpi radialis & ulnaris (flex the wrist)
Extensor carpi radialis & ulnaris (extend the wrist)
Flexor/extensor digitorum (move the fingers)
🖐️ These muscles are crucial for grip strength, fine motor control, and daily tasks like writing, holding objects, or using tools.
🧰 Why Arm Muscles Matter in Daily Life
From carrying bags to opening jars or pushing a shopping cart, strong arm muscles make everyday tasks easier and safer. Well-developed biceps, triceps, and forearms:
🛡️ Prevent injury by supporting joints
🧍 Improve posture and balance
🎯 Increase precision in hand movements
🏆 Enhance athletic performance
Even if you’re not lifting weights daily, training your arms improves quality of life by making routine actions more efficient and less tiring.
🔥 Best Exercises for Biceps
To build impressive biceps, you need isolation and compound exercises that target both heads.
✅ 1. Barbell Curls
Grip: Underhand, shoulder-width
How: Curl the bar to shoulder height without swinging your body
Benefits: Builds mass and strength in both biceps heads
✅ 2. Dumbbell Curls
Allows for greater range of motion
Great for correcting muscle imbalances
Try alternating or concentration curls for added focus
✅ 3. Hammer Curls
Grip: Neutral (palms facing each other)
Targets: Biceps + brachialis + forearm
Boosts overall arm thickness
🎯 Tip: Squeeze at the top of each rep and lower slowly for max muscle activation.
🧨 Best Exercises for Triceps
The triceps make up nearly two-thirds of your upper arm size—training them is key for full arm development.
✅ 1. Triceps Dips
Equipment: Dip bars or a bench
How: Lower your body by bending elbows, then push back up
Engages: Triceps, chest, and shoulders
✅ 2. Overhead Triceps Extensions
Use: Dumbbells or cables
Great for stretching and strengthening the long head
Keep elbows close to your ears for proper form
✅ 3. Skull Crushers
Lying down with dumbbells or an EZ-bar
Lower weights toward your forehead, keeping upper arms still
Intense isolation for triceps hypertrophy
🚫 Avoid flaring elbows out too wide—focus on form over heavy weight!
💥 Effective Forearm Exercises
Strong forearms equal strong grip—and better performance in nearly every upper body move.
✅ 1. Wrist Curls
Seated, forearms on thighs
Palms up, curl the dumbbells using just your wrists
Builds the flexor muscles of the forearm
✅ 2. Reverse Curls
Overhand grip on a barbell or dumbbells
Engages the extensor muscles and brachioradialis
✅ 3. Grip Trainers & Static Holds
Use hand grip tools or heavy dumbbells
Hold for time or perform repetitions
Great for rock climbers, tennis players, or lifters
🧠 Pro Tip: Don’t neglect wrist mobility—stretching and rolling can prevent overuse injuries.
🏋️ Balanced Arm Training Routine
For balanced muscle development, aim to hit each arm group 2x per week with a variety of exercises. Here’s a sample split:
| Day | Focus |
|---|---|
| Monday | Biceps + Forearms |
| Wednesday | Triceps + Core |
| Friday | Full Arm Superset Day |
Each session should include:
2–3 biceps exercises
2–3 triceps exercises
1–2 forearm/grip-focused movements
Reps/sets:
8–12 reps for muscle growth (hypertrophy)
4–6 reps with heavier weights for strength
15–20 reps for endurance or isolation work
⚠️ Common Arm Training Mistakes
Avoid these errors to get the best results:
❌ Using momentum or swinging weights
❌ Neglecting full range of motion
❌ Ignoring triceps in favor of biceps
❌ Overtraining without enough rest
🎯 Focus on slow, controlled reps, and prioritize mind-muscle connection—especially during isolation movements.
🧑⚕️ Expert Insight
“If you want bigger arms, train your triceps just as hard as your biceps. Most people don’t realize triceps give your arms their size.”
– Coach David H., Certified Strength Trainer
“Wrist and grip strength are underrated but essential for longevity and injury prevention, especially in athletes and lifters.”
– Dr. Jennifer King, Sports Physio
🏁 Conclusion: Build Stronger, Balanced Arms
Strong, defined arms are about more than just flexing in the mirror—they’re about power, control, and performance. By understanding the anatomy and function of the biceps, triceps, and forearms, you can tailor your workouts for better results and a more functional physique.
Whether you’re lifting weights, playing sports, or just living your life—well-developed arm muscles improve everything you do 💯.
So grab those dumbbells, focus on proper form, and commit to balanced arm training. Your future self will thank you 💥.
What makes this video truly valuable is not just the list of artery-cleansing foods, but how Dr. Berg breaks down their biological impact. He explains how specific nutrients in garlic, turmeric, leafy greens, and omega-3-rich foods actively reduce inflammation, support nitric oxide production, and improve arterial flexibility.
Unlike generic health advice, this video offers a science-backed approach to natural cardiovascular support — perfect for anyone looking to reduce arterial plaque and support heart health naturally. It’s clear, practical, and based on real physiology.
I highly recommend incorporating these foods as part of a long-term lifestyle strategy, especially for individuals seeking preventive heart care without relying entirely on medication.